Antoine Lavoisier Biography
Early Life:
Antoine-Laurent Lavoisier was born in August of 1743 in Paris, France. His father was a lawyer, who worked in Parliament. As a result, Lavoisier’s family was quite wealthy as he grew up.
Let’s explore some facts about this great man!
At age 11, Lavoisier enrolled in a college from the University of Paris, Collège des Quatre-Nations.
There, his studies included multiple different topics, but he leaned towards the study of science in his last two years at the college, before graduating at the age of 18.
Despite the fact that Lavoisier was very interested in studying Science, he wanted to follow in his father’s footsteps and study law at university. This was also likely because of his father’s wishes.
Therefore, at 18 Lavoisier enrolled in law school at the University of Paris.
At the University of Paris, Lavoisier earned his bachelor’s degree in law within 2 years. The following year he earned his license to practice law professionally.
It was then that he decided not to follow through with this plan of becoming a lawyer.
During the time that Lavoisier spent studying law, he was also spending his spare time in science lectures and working on his own research.
In the same year that he earned his legal license, he also published his own scientific paper.
Five years after his very first scientific publication, he was granted membership into the French Academy of Sciences. He was only 26 at the time.
Scientific Discovery:
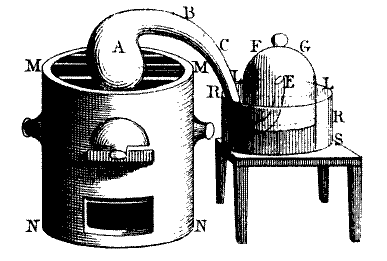
In the year 1772, Lavoisier performed an experiment on a diamond, in which they put it in a glass jar and focused a large magnifying glass on it under the sun.
They found that the diamond ended up burning away to nothing.
Importantly, Lavoisier noticed the that the weight of the jar didn’t decrease, which later helped him realize the law of conservation of mass.
This law states that mass cannot change in a system that is unaffected by matter and energy changes.
Additionally, the burned diamond produced a gas, which we now call carbon dioxide. This also helped Lavoisier understand that diamonds and charcoal are from the same element, which he called carbon.
Another scientific discovery that Lavoisier made were understanding combustion, which is the reaction of certain substances with oxygen at appropriately high temperatures.
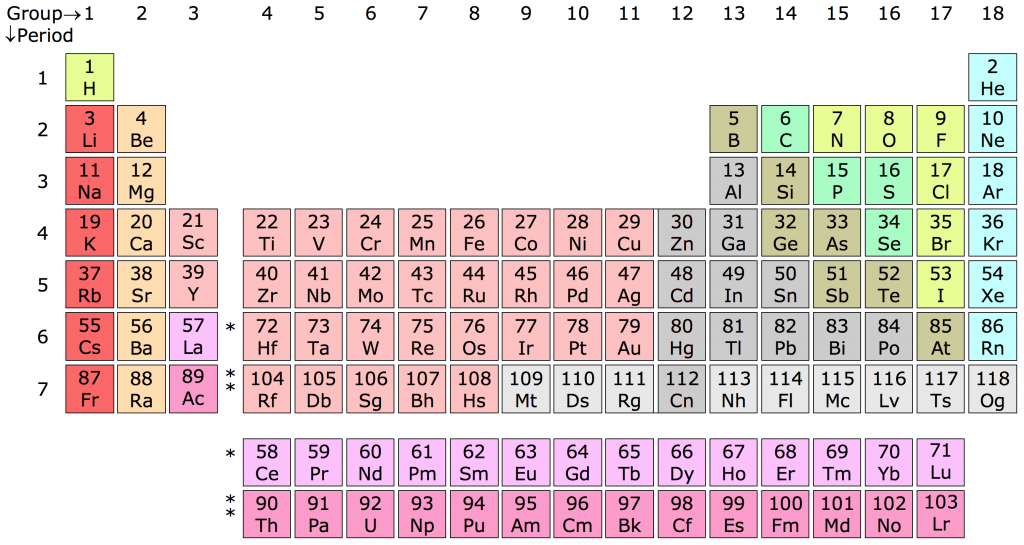
In fact, Lavoisier is the scientist that discovered and named the elements oxygen, hydrogen, and sulfur.
Impact:
Lavoisier was one of the first scientists to disprove Aristotle’s ideas of only 4 elements (earth, air, fire, and water).
He published a book entitled Elementary Treatise on Chemistry, describing the actual elements he discovered that we now know as part of the periodic table of elements.
This book listed the elements that he contributed to the discovery of, including carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, sulfur, nitrogen, copper, gold, manganese, phosphorous, and interestingly, light (which we now know is not an element).
Later Years:
Unfortunately, Lavoisier, along with the French Academy of Sciences, was a victim of the French Revolution, in which French citizens targeted the wealthy.
He died in 1794. In the following year, the French government proclaimed him innocent.