Parts Of A Flower For Kids

Flowers are one of the symbols of beauty, and they are used for decorations to improve their aesthetic value during special occasions like festivals, weddings, housewarming ceremonies, etc. they emanate fragrance which gives us a pleasant feel. It represents a variety of emotions and feelings, like compassion, love, friendship, divinity, etc.
If you pay attention and study flowers, you will be astonished at how beautiful and intelligent nature is! The study of flowers, their cultivation, and their applications are called floriculture.
Also Read: Plant Life Cycle For Kids
12 Fascinating facts about the parts of a flower
Stigma plays an active role in checking compatibility.
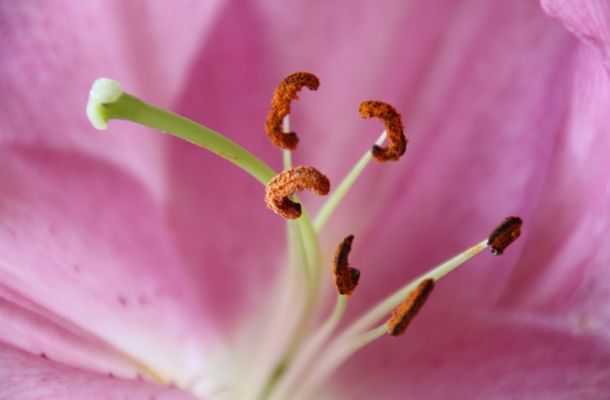

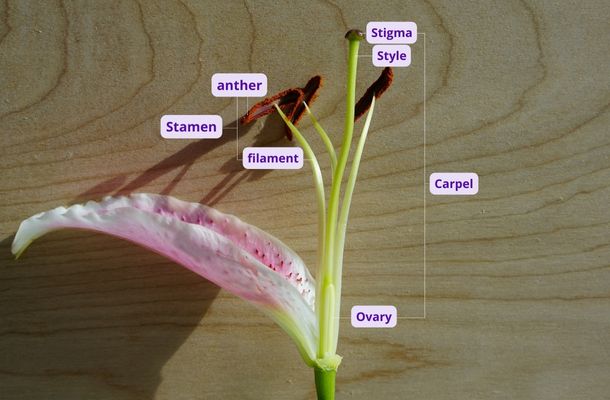
Stigma is the uppermost part of the pistil, and its function is to receive or capture pollen. It is sticky and contains hair-like structures that help capture pollen carried by wind or insects. Stigma hydrates pollen grains which are dry when they leave another. Now, the hydrated pollen grain forms a pollen tube that penetrates through stigma and style towards the ovary. Stigma plays an active role in checking compatibility, wherein the pollen gets rejected when identified as different species.
Ovaries may be unilocular, bilocular, trilocular, or multilocular

The ovary is the part of the pistil that houses the ovule. It is at the point of connection with the base of petals and sepals. It has compartments called locules; each locule contains one or more ovules. Ovaries may be unilocular, bilocular, trilocular, or multilocular depending on the number of locules.
The ovule, also called megasporangium, contains a female gamete called megaspore in the center. Megaspore develops from a megaspore mother cell. A series of different types of cell division transforms the mother cell into a megaspore. Ovules attach to the inner wall of the ovary at places called placentae (singular: placenta).
After pollination, pollen grains germinate and protrude as pollen tubes into the pistil from stigma, through style, and reach the ovary, which releases microspores. Megaspores in the ovule fuse with microspores, and the process are called fertilization. After fertilization, the ovule develops into seeds, and the ovary transforms into fruit.
Sepals provide support to the petals when flowers bloom.

Sepals are green-colored, leaf-shaped structures that form the exterior part and protect the interior organs of a flower in the bud stage. They provide support to the petals when flowers bloom. In most fully matured flowers, sepals are smaller in size than petals.
In some plants, sepals wither from the flower after they bloom. In contrast, sepals in some species grow until they form a bladder-like envelope around the fruit to protect it from being eaten by birds and animals.
The anther is the structure in which Male gametes form.
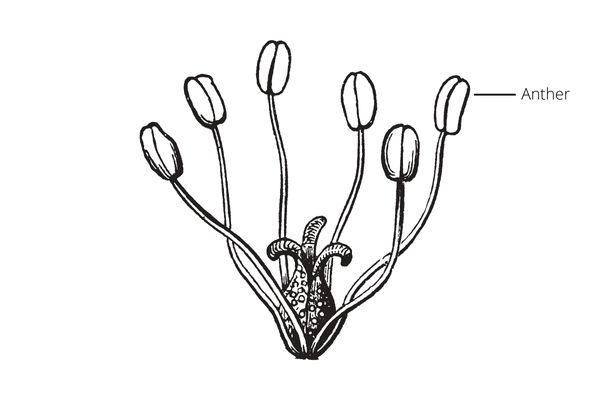
The anther is the structure in which male gametes form. It contains two pollen sacs, which are also called microsporangia (singular: microsporangium). Each pollen sac has two chambers called locules which enclose male gametes called microspores. Microspores form by multiple cycles of cell division of cells called microspore mother cells. One of the significant differences between microspores and their mother cells is the number of chromosomes.
Petals are the most significant parts of flowers.
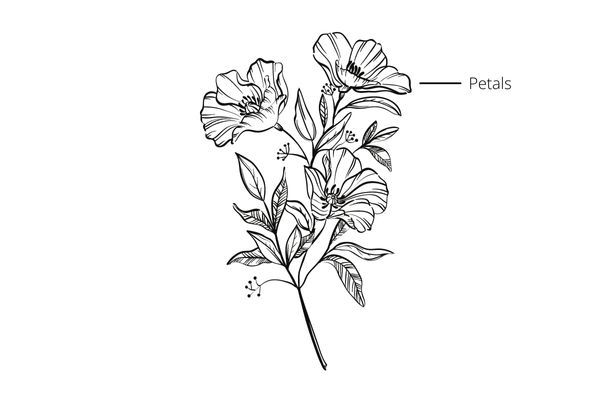
Petals are the most significant and most prominent parts of flowers. They are often brightly colored, and their size and shape vary widely across species. Scent and color are the two attributes of petals that contribute to pollination. The scent attracts pollinators, such as insects, including moths, bees, and flies. Colors create contrast with the background and attract not only insects but also birds and animals.
Petals have two parts: a broad upper part called the blade and a narrow lower part called the claw. Claw, in most plants, is whitish, unlike the blade, which is brightly colored. The claw and blade are at an angle to each other.
The life span of plants
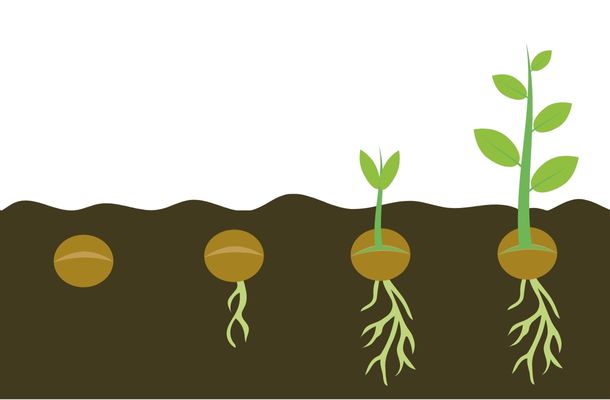

Some plants bloom with short photoperiods, and they are called short-day plants. Examples of long-day plants are spinach and Rose-of-Sharon. Some plants do not flower until age; for example, a sugar maple tree may not flower until 30.
Also read: Photosynthesis Facts
Flowers look simple but have complex structures.
Flowers look simple but have complex structures seen when dissected and observed closely. Parts of a flower are classified into vegetative and reproductive functions.
- Reproductive parts: the structures in the flower that interact with each other to form seeds are called reproductive parts. The pistil and stamen are the reproductive parts.
- Vegetative parts: are structures or organs that do not directly participate in reproduction.. However, they are crucial for the events that make reproduction possible.
Pedicel carries the weight of the flower.

The pedicel is the stalk or stem of a flower that supports the growth, carries the weight of the flower, and allows it to stay in the air. When flowers are present in clusters, the pedicel attaches to a stalk called a peduncle.
The pistil is the female reproductive part and forms the central part of a flower.

The pistil is the female reproductive part and forms the central part of a flower. There may be one or more pistils, which are collectively called gynoecium. Pistils are bowling-pin-shaped structures and comprise three forms: stigma, style, and ovary.
Stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower.

Stamen is the male reproductive part of a flower. Filament and anther are two parts of Stamen. Stamens are collectively called androecium, and the number varies across species from a half-stamen to a few thousand. In most species, stamens surround the female reproductive part of the flower, and perianth surrounds stamens.
Lilly, cherry blossom, and the flower of apples are perfect flowers.

A flower that has either stamen or pistil is called an imperfect flower. It is a unisexual flower because it has only one of the two reproductive parts. Lilly, cherry blossom, and flower of apples are some examples of perfect flowers.
Flowers of cucumber, walnut, and begonia are some imperfect flowers.
A flower that possesses both stamen and pistil is called a perfect flower. It is a bisexual flower because it has all two reproductive parts. Flowers of cucumber, walnut, and begonia are some imperfect flowers.
Also Read: 6 Parts of Plants for Kids
Conclusion
The structure of flowers varies significantly across the plant species and goes through several elaborate processes from their initiation to transformation into a fruit. Undoubtedly, they are one of the wonders nature has produced.
Want to know more interesting facts about other topics? Continue reading Cool Kid Facts!
